In today’s fast-paced enterprise environment, real-time decision-making has become a critical capability. Businesses face dynamic challenges ranging from fraud detection and supply chain disruptions to customer service inquiries that demand instant and accurate responses. Traditional centralized systems often struggle to cope with these demands due to data volume, complexity, and speed requirements.
This is where multi agent architectures come into play offering a powerful approach to distributed intelligence that can drive faster, more reliable decisions.
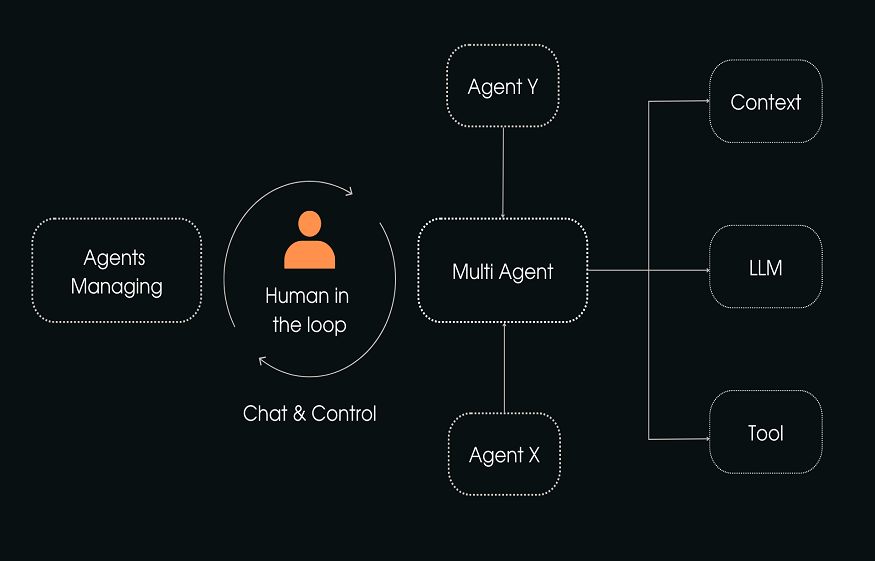
Understanding Multi-Agent Architectures
At its core, a multi-agent architecture consists of multiple autonomous agents—software entities that perceive their environment, make decisions, and act independently or collaboratively. Each agent typically specializes in a specific task or function, communicating and coordinating with other agents to achieve broader objectives.
Agents can be reactive (responding immediately to changes), deliberative (planning and reasoning before acting), or hybrid (combining both capabilities). Communication between agents relies on well-defined protocols that ensure information flows smoothly, enabling them to negotiate, share data, or request assistance. This decentralized and modular design contrasts sharply with monolithic, centralized systems, providing flexibility and scalability critical for enterprise operations.
Real-Time Decision-Making Needs in Enterprises
Enterprises operate in environments where decisions must be made instantly and accurately. Consider examples like:
- Fraud detection in banking, where suspicious transactions must be flagged within seconds.
- Supply chain optimization, requiring real-time inventory updates and dynamic routing to prevent delays.
- Customer support, where AI-powered chatbots need to respond immediately to customer inquiries while escalating complex issues appropriately.
- Compliance monitoring, involving continuous checks against evolving regulatory requirements like GDPR or HIPAA.
These scenarios involve massive data inflows from diverse sources, requiring fast integration, analysis, and response. Traditional centralized architectures often bottleneck at processing speed or fail to provide the adaptability enterprises need in complex workflows.
How Multi-Agent Architectures Enable Real-Time Responses
Multi-agent architectures enable real-time responses in enterprises by distributing workloads across multiple autonomous agents that operate simultaneously. Unlike centralized systems, where tasks are processed sequentially, these architectures allow specialized agents to handle different parts of a workflow in parallel. This decentralized approach significantly reduces delays and improves processing speed, making it ideal for environments where timely decisions are critical.
Each agent has the ability to make independent decisions based on real-time data relevant to its specific function. For example, in fraud detection, an agent can immediately block suspicious transactions without waiting for centralized approval, while other agents analyze market data or compliance risks concurrently. This autonomy allows the system to respond swiftly to varied and complex scenarios, while continuous monitoring enables agents to share updates and alerts across the network to maintain coordination.
Through ongoing communication and collaboration, multi-agent systems adapt dynamically to changing conditions. In practical terms, if a supply chain agent detects a shipment delay, it can alert logistics agents to reroute deliveries automatically. This seamless information flow and coordinated action create a resilient, efficient network that handles complex, multi-step workflows with minimal human intervention—ultimately enabling enterprises to operate with greater speed, accuracy, and agility in real time.
Benefits of Multi-Agent Architectures for Real-Time Decisions
Adopting multi-agent architectures offers several key benefits that address the complex demands of modern enterprises.
Scalability: One of the greatest strengths is the ability to scale efficiently. Agents can be added or removed seamlessly as business needs evolve, allowing the system to handle growing volumes of data and increasing complexity without compromising performance. This flexibility ensures that enterprises can respond quickly to market changes or sudden spikes in workload.
Fault Tolerance: Multi-agent systems are inherently resilient. Because tasks are distributed among autonomous agents, the failure of one component does not bring down the entire system. Other agents continue their functions uninterrupted, maintaining overall system stability and minimizing downtime. This fault tolerance is critical for mission-critical operations where continuous availability is essential.
Speed and Accuracy: The parallel processing capabilities of multi-agent architectures accelerate decision-making by enabling multiple agents to work on different tasks simultaneously. Coupled with local decision-making, this approach reduces latency and improves the precision of outcomes. Agents specialized in their domains can apply contextual knowledge to make more accurate judgments faster than centralized systems.
Complex Workflow Handling: Multi-agent systems excel at managing workflows that involve multiple interdependent steps. Each agent can handle specific tasks independently while communicating and coordinating with others to ensure consistency, completeness, and compliance with business rules. This distributed control streamlines complex processes that would otherwise require extensive manual intervention.
Collectively, these advantages translate into significant operational improvements, enabling enterprises to stay agile, competitive, and better equipped to handle the demands of real-time decision-making in dynamic environments.
Use Cases in Enterprise Domains
Financial Services: Multi-agent architectures are essential for real-time fraud detection in financial services. Agents monitor transactions across regions and channels, quickly identifying suspicious patterns like unusual spending or login behavior.
For example, one major bank uses multi-agent systems to reduce fraud losses by automatically blocking high-risk transactions while alerting human analysts for review. This setup also helps meet strict regulatory requirements such as AML and KYC efficiently.
Supply Chain Management: In supply chains, agents continuously track inventory, shipments, and supplier statuses. When disruptions occur—such as a delayed shipment caused by bad weather—agents dynamically adjust routes and delivery schedules to minimize impact.
For instance, a global retailer leverages multi-agent systems to optimize last-mile delivery by rerouting packages in real time, improving customer satisfaction and reducing costs.
Customer Service: AI chatbots work in tandem with backend agents that manage ticket routing and resolution workflows. This ensures immediate customer engagement and smooth handoffs to human agents when necessary. Companies using this approach have reported faster response times and higher customer satisfaction scores.
Compliance and Risk Management: Enterprises use specialized agents to monitor transactions and communications, flagging potential compliance risks automatically.
For example, a healthcare provider uses multi-agent systems to ensure patient data handling complies with HIPAA, adapting quickly to updated privacy regulations without downtime.
Additional Applications: Other sectors like manufacturing and IT operations benefit from multi-agent systems for automating quality control, equipment monitoring, and incident management, enhancing efficiency and reliability across complex workflows.
Key Technical and Organizational Factors for Successful Multi-Agent Architecture Implementation
Implementing multi-agent architectures in enterprise environments holds immense promise, but it also requires thorough planning and coordination across technical and organizational domains.
Seamless Integration: Multi-agent systems must integrate smoothly with existing IT infrastructure and enterprise applications. This involves ensuring compatibility with legacy systems, APIs, and data sources to enable agents to access real-time information and act effectively without causing disruption or data silos.
Robust Security and Compliance: Since agents continuously share and process sensitive data, protecting this information is critical. Enterprises must implement stringent security protocols to safeguard data transmission and storage, adhering to industry regulations such as GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA. Secure authentication, encryption, and access controls are fundamental to preventing breaches and maintaining compliance.
Effective Coordination and Communication: To prevent duplicated efforts, conflicting actions, or communication breakdowns among autonomous agents, enterprises need clear communication protocols and conflict resolution mechanisms. Designing a framework where agents share state, negotiate task assignments, and synchronize decisions is vital for coherent and efficient workflow execution.
Comprehensive User Training and Change Management: Employees must understand how multi-agent systems function and learn to collaborate effectively with autonomous agents. Providing training programs that demystify AI decision-making, clarify when human intervention is necessary, and build trust in the technology is essential. Moreover, cultivating a culture open to automation and innovation helps ease adoption and maximize impact.
Scalability and Maintenance Planning: Enterprises should also plan for the ongoing maintenance, updates, and scaling of their multi-agent systems. As business needs evolve, the architecture must be flexible enough to add or modify agents without causing downtime or degradation in performance.
By proactively addressing these technical and organizational factors, enterprises can harness the full power of multi-agent architectures, boosting operational agility, reliability, and overall effectiveness in complex, real-time workflows.
Future Trends and Innovations in Multi-Agent Architectures
As enterprise demands grow more dynamic and distributed, multi-agent architectures are poised to evolve in transformative ways. Several emerging trends and innovations are shaping the next frontier of enterprise AI:
Agentic Language for Better Human-AI Collaboration: Future agents will be equipped with more natural, agentic language capabilities—communicating intentions, limitations, and actions in ways that feel intuitive and human. This evolution in language design will help build trust, reduce cognitive load, and create smoother collaboration between agents and employees.
Adaptive and Continual Learning: Agents will become more autonomous by learning from their environments and historical interactions. Rather than relying solely on static rules or retraining cycles, adaptive agents will fine-tune their behavior over time, improving decision quality, anticipating user needs, and responding more intelligently to new challenges.
Edge Computing and IoT Integration: As enterprises increasingly rely on edge devices and IoT sensors, integrating multi-agent systems with edge computing will unlock faster, localized data processing. Agents operating closer to the data source can make time-sensitive decisions, such as adjusting factory machinery or rerouting delivery vehicles, without waiting for centralized approval.
Cross-Enterprise Agent Collaboration: Looking beyond internal operations, multi-agent systems will facilitate collaboration across organizational boundaries. For example, logistics agents from different companies might coordinate delivery schedules, or compliance agents could automatically reconcile regulatory requirements between partners, streamlining ecosystems and improving transparency.
These innovations will not only amplify the speed and intelligence of enterprise decision-making but also redefine how businesses structure their digital operations. Multi-agent architectures are not just tools—they’re becoming strategic frameworks for building adaptive, intelligent, and scalable enterprises.
Conclusion
Multi-agent architectures are reshaping how enterprises make decisions in real-time. By distributing tasks across intelligent, autonomous agents, organizations can respond faster to changing conditions, reduce bottlenecks, and improve operational resilience. These systems enable smarter collaboration between humans and machines—making enterprise workflows more adaptive and efficient.
As real-time responsiveness becomes a competitive requirement, adopting multi-agent systems is no longer optional for forward-looking businesses. From fraud detection to supply chain optimization and customer service, the benefits are already visible across industries.
Looking ahead, innovations like agentic language, adaptive learning, and edge integration will make these architectures even more powerful. Enterprises that embrace this shift early will be better positioned to navigate complexity, drive innovation, and build scalable, AI-driven operations.